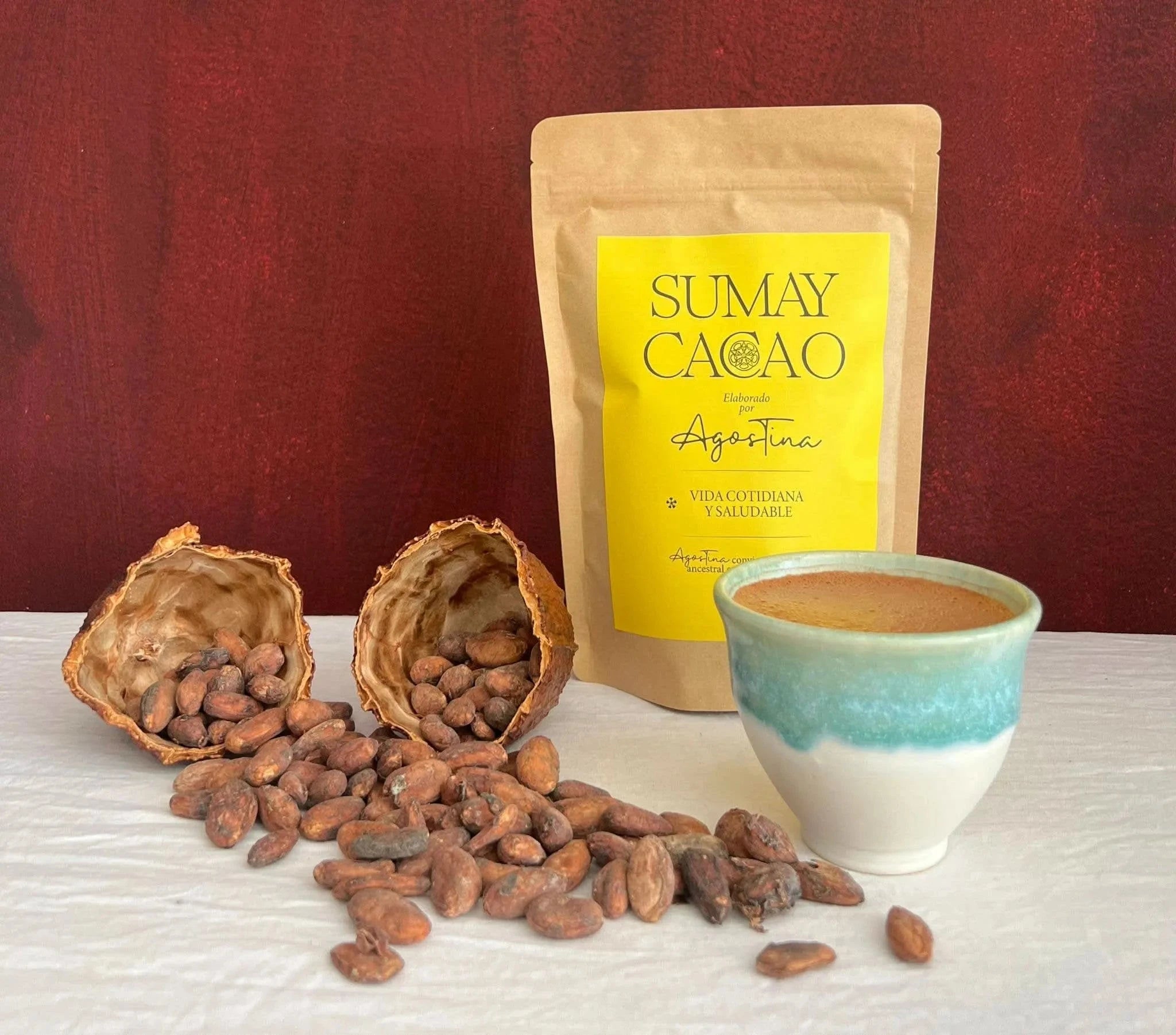
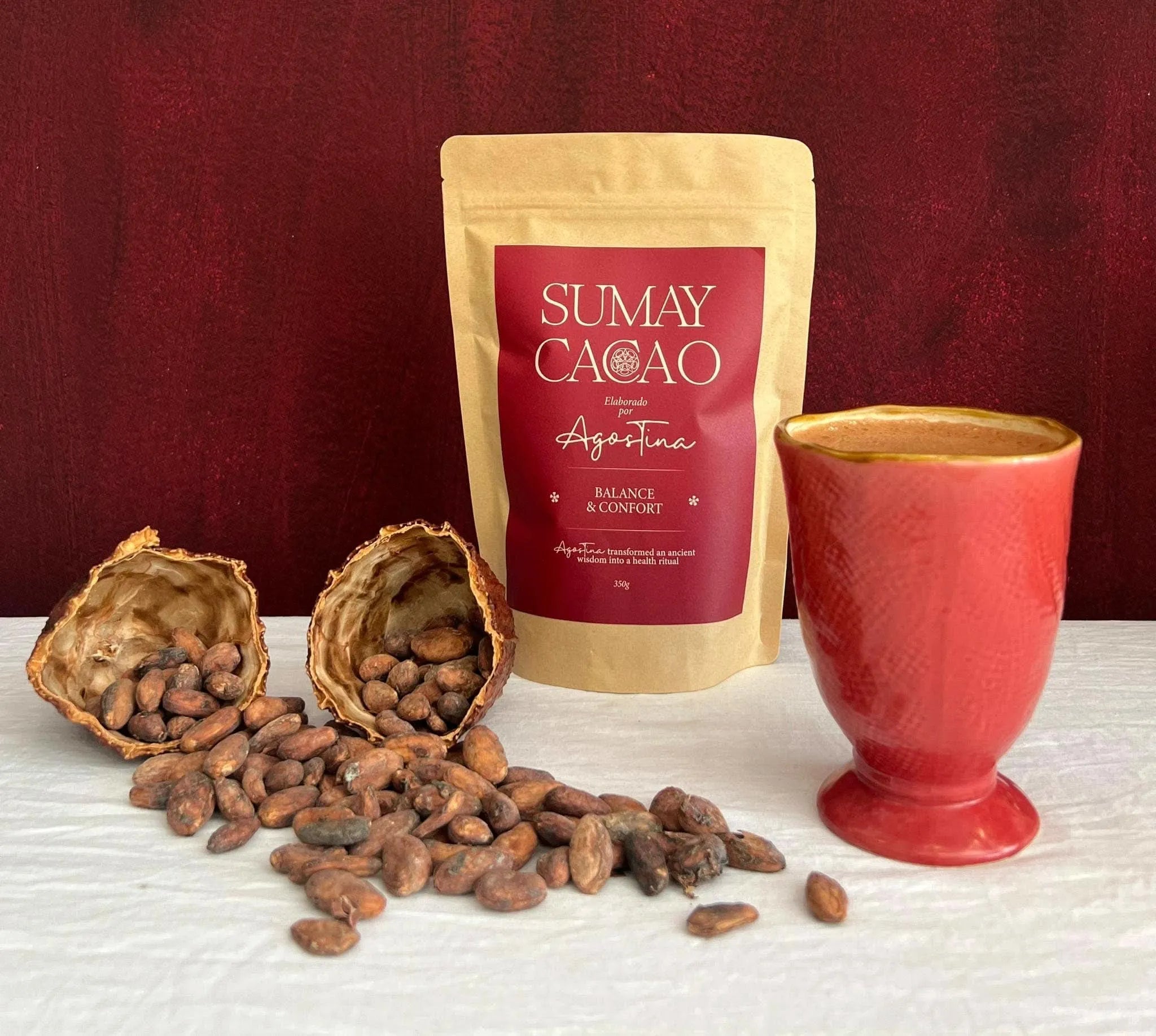
Natural Supplements
Filter
Sort by:
Description
Natural Supplements: Composition, Sources, and Bioactive Properties
Natural supplements derive from plant, animal, and microbial sources, containing concentrated bioactive compounds that support physiological functions. These formulations provide specific nutrients, phytochemicals, and functional ingredients in standardized concentrations, allowing for precise dosing and targeted nutritional support beyond conventional food sources.
The extraction and processing methods significantly influence supplement potency and bioavailability. Cold-pressed botanicals preserve temperature-sensitive compounds, while standardized extracts ensure consistent active ingredient concentrations across production batches. Fermentation processes enhance certain compounds' bioavailability by breaking down complex molecules into more readily absorbed forms.
Quality indicators for natural supplements include standardization percentages of active constituents, third-party testing verification, and certificate of analysis documentation. Premium formulations utilize full-spectrum extracts containing synergistic compounds that enhance overall effectiveness compared to isolated components.
Supplement forms vary based on absorption requirements and target applications. Fast-dissolving powders provide rapid absorption, while time-release capsules deliver sustained compound release. Liposomal delivery systems encapsulate water-soluble nutrients within phospholipid membranes, significantly improving bioavailability for compounds with typically poor absorption profiles.
Natural supplements provide targeted nutritional support with precise active compound concentrations unavailable through conventional food sources, offering complementary approaches to address specific health objectives when incorporated within comprehensive wellness protocols.
Types
Primary Natural Supplement Categories and Formulations
Botanical and Herbal Extract Classifications
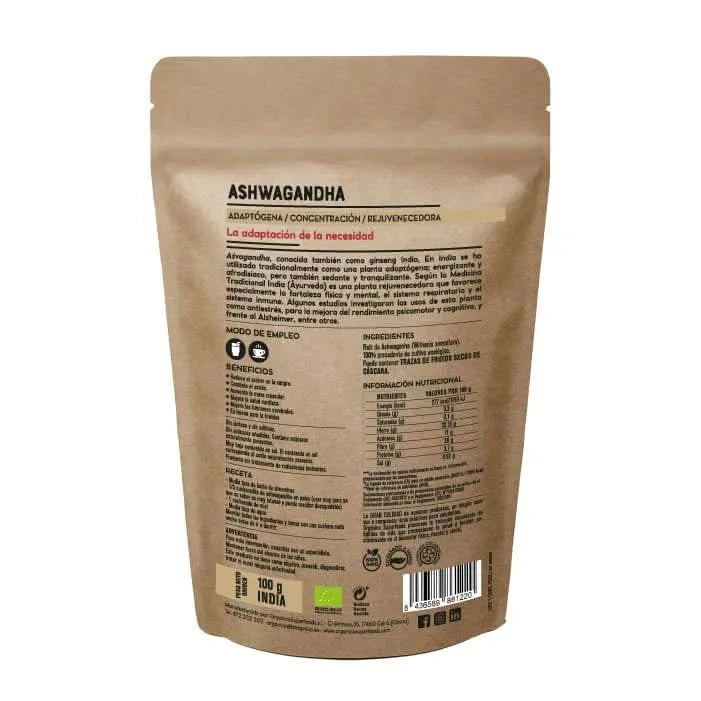
Adaptogenic herbs represent plant-based supplements that help the body respond to various stressors, maintaining physiological homeostasis. Key examples include Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) containing withanolides that modulate cortisol production, Rhodiola rosea with active compounds rosavins and salidroside supporting mental energy, and Panax ginseng featuring ginsenosides that enhance cellular energy production. These botanical extracts undergo specific harvesting and processing protocols to preserve their bioactive components, with standardization ensuring consistent potency across batches.
Nutritional Supplements and Essential Compounds
Vitamin supplements provide essential micronutrients in various forms that significantly impact bioavailability. Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) require dietary fat for optimal absorption and undergo different metabolic pathways than water-soluble varieties. Mineral supplements address specific deficiencies with varying absorption rates based on their chemical form, with chelated minerals demonstrating superior bioavailability compared to inorganic forms. Amino acid supplements deliver protein building blocks in free-form configurations that bypass digestive breakdown requirements, providing rapid absorption for tissue repair and physiological functions.
Microbial-Based Formulations
Probiotic supplements contain live beneficial microorganisms primarily from Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Saccharomyces genera, formulated with specific colony-forming unit (CFU) counts indicating viable organisms per dose. Different strains demonstrate unique physiological effects based on their genetic profile, with targeted formulations addressing specific body systems. Strain identification requires precise taxonomy using genus, species, and strain designation (e.g., Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM), with research validating specific strain benefits rather than general species effects. Prebiotic supplements provide non-digestible fiber compounds that selectively feed beneficial intestinal bacteria, enhancing their colonization and metabolic activities.
Benefits
Natural Supplement Health Benefits and Mechanisms
Cognitive Function and Neurological Support Mechanisms
Ginkgo biloba extract contains flavonoid glycosides and terpene lactones that enhance cerebral microcirculation through vasodilation and reduced blood viscosity, improving oxygen and glucose delivery to brain tissues. Clinical research demonstrates its effectiveness in age-related cognitive decline through enhanced mitochondrial efficiency and decreased oxidative damage in neuronal cells. Bacopa monnieri (Brahmi) delivers bacosides that modulate neurotransmitter production while supporting dendritic branching in hippocampal neurons, enhancing synaptic communication pathways critical for memory formation. This adaptogenic herb demonstrates cumulative effects with consistent 8-12 week administration, improving information processing speed and working memory capacity.
Immune Function and Inflammatory Response Regulation
Medicinal mushroom extracts including Reishi (Ganoderma lucidum), Turkey Tail (Trametes versicolor), and Maitake (Grifola frondosa) contain beta-glucan polysaccharides that modulate immune cell activity through specific membrane receptor binding. These compounds increase natural killer cell cytotoxicity and macrophage activation without overstimulating inflammatory pathways. Curcumin from Turmeric (Curcuma longa) inhibits multiple inflammatory signaling pathways including NF-?B, COX-2, and specific cytokine cascades, reducing inflammatory marker expression. Its poor natural bioavailability necessitates specialized delivery systems such as phospholipid complexes or black pepper extract (piperine) co-administration to achieve therapeutic blood concentrations.
Cardiovascular System and Metabolic Health Support
Berberine, an alkaloid compound derived from plants including Berberis aristata and Coptis chinensis, activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathways similar to certain pharmaceutical agents. This activation improves insulin sensitivity, reduces hepatic glucose production, and enhances glucose uptake in peripheral tissues. Clinical research demonstrates comparable effects to conventional approaches for metabolic parameter management. Plant sterols and stanols, structurally similar to cholesterol, compete for intestinal absorption sites, reducing cholesterol uptake by approximately 10-15% when consumed at 2-3g daily doses. These compounds demonstrate additive benefits when combined with other cardiovascular support approaches through complementary mechanisms of action.
Instructions
Natural Supplement Preparation Methods and Storage Guidelines
Extraction Techniques and Processing Methodologies
Water-based extraction methods utilize precise temperature control to isolate water-soluble compounds from botanical materials. Cold infusion techniques (steeping at room temperature for 4-12 hours) preserve heat-sensitive compounds, while hot infusions extract more constituents but may degrade certain thermolabile components. Decoctions require simmering tougher plant materials like roots and bark for 15-45 minutes to release deeply embedded compounds. Alcohol-based extractions (tinctures) use varying ethanol percentages (20-95%) to extract both water-soluble and alcohol-soluble compounds, with higher alcohol concentrations extracting more resins, essential oils, and alkaloids while preserving the preparation without additional preservatives.
Formulation Stability and Storage Requirements
Natural supplements require specific storage conditions to maintain potency and prevent degradation. Temperature fluctuations accelerate oxidative processes, with most products maintaining optimal stability between 59-77°F (15-25°C). Light exposure degrades photosensitive compounds like riboflavin, carotenoids, and certain alkaloids, necessitating amber or opaque containers. Humidity levels above 60% may trigger premature degradation through hydrolysis reactions or microbial growth, particularly in powdered formulations. Oxygen exposure initiates oxidation in compounds with unsaturated bonds, including essential fatty acids and certain phytochemicals, making vacuum-sealed or nitrogen-flushed packaging essential for these sensitive ingredients.
FAQs